Most WordPress site owners view errors as overwhelming disasters that demand expert help. A 500 Internal Server Error makes them think, “I need to hire someone.” A blank white screen? They assume their site is ruined forever.
But here’s the truth from someone who’s fixed thousands of WordPress errors. How to Fix the Most Common WordPress Errors (Without Breaking Your Site)
90% of common WordPress issues have simple fixes that take just 5-15 minutes – even for non-technical users.
The White Screen? Usually caused by two plugins clashing. Solve it by disabling the plugins via FTP. Database Connection Errors? Often, it’s just a typo in your WP-config.php file, easy to fix with a text editor. 404 errors on all pages? Likely due to corrupted permalinks, which you can regenerate with two clicks in WordPress settings.
The errors seem daunting, but the solutions are simple.
This guide walks you through troubleshooting 23 of the most common WordPress errors in 2026. Each error includes:
- A simple explanation of what it means.
- The most likely causes (ranked by probability).
- Step-by-step fixing instructions with screenshots.
Prevention tips to avoid future issues.
Whether your site is completely down or you’re just seeing warnings, you’ll find a clear solution.
Let’s start with the error that causes the most panic.
What are WordPress Errors?
WordPress errors are issues that stop your site from working correctly. They can be minor problems, like failed file uploads, or big ones, like a complete site crash that locks you out of your dashboard.
These errors can occur for various reasons: plugin conflicts, theme issues, server limits, corrupted databases, or incorrect file permissions. Knowing the type of error you’re dealing with is the first step to fixing it quickly.
The good news? Most WordPress errors follow patterns and have proven solutions. Fixing them quickly can help protect your site traffic and search rankings.
Why Fixing WordPress Errors Quickly Matters
Indeed, here are five key points highlighting the importance of troubleshooting WordPress errors:
- Visitors bounce when sites break
A white screen or 500 error doesn’t just frustrate you – it sends visitors straight to your competitors. Studies show 88% of users won’t return to a site after a bad experience.
- Search rankings drop fast.
Google regularly checks your site. If it repeatedly finds errors, your rankings suffer. A site that’s down for just a few hours can lose weeks of SEO progress.
- Security vulnerabilities widen
Some errors expose security holes. Leaving database connection errors unfixed, for example, can signal weak credentials to attackers scanning for vulnerable sites.
- Emergency fixes cost more.
Catching errors early means simple DIY fixes. Waiting until your site crashes during a product launch means expensive emergency developer fees and lost revenue.
- Trust disappears quickly
Professional sites don’t show error messages. Users equate broken websites with unreliable businesses. One “connection timed out” error can permanently cost you a customer.
WordPress Errors Quick Reference Guide
| Error Type | Status Code | What You’ll See | Main Cause | Quick Fix |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White Screen of Death | None | Blank white screen, no content | Plugin conflicts, theme breaks, PHP memory exhausted | Disable plugins via FTP, increase memory limit |
| Bad Request | 400 | “400 Bad Request” | Mistyped URL, browser cache issues, server errors | Clear cache/cookies, check URL, flush DNS |
| Forbidden | 403 | “403 Forbidden – Access Denied.” | Incorrect file permissions, .htaccess rules, security plugins | Set directories to 755, files to 644, regenerate .htaccess |
| Not Found | 404 | “404 Page Not Found” | Page doesn’t exist, broken links | Fix broken links, use redirects |
| Method Not Allowed | 405 | “405 Method Not Allowed” | Server rejects request method | Check recent updates, server settings |
| Request Too Large | 413 | “413 Request Entity Too Large” | Upload file too large | Increase maximum request size |
| Too Many Requests | 429 | “429 Too Many Requests” | Multiple access attempts blocked | Change login URL, test for conflicts |
| Internal Server Error | 500 | “500 Internal Server Error” | Multiple causes, hard to diagnose | Clear cache, reload page, pursue technical fixes |
| Not Implemented | 501 | “501 Not Implemented” | Server doesn’t support request | Reload page, clear cache, contact host |
| Bad Gateway | 502 | “502 Bad Gateway” | Server communication failure | Reload page, check DNS, contact host |
| Service Unavailable | 503 | “503 Service Unavailable” | Server up but unreachable | Disable plugins, change to basic theme, check resources |
| Gateway Timeout | 504 | “504 Gateway Timeout” | Servers can’t communicate | Reload, disable CDN, check DNS settings |
| Memory Limit Error | Fatal Error | “Allowed memory size exhausted” | PHP memory limit exceeded | Add define(‘WP_MEMORY_LIMIT’, ‘256M’) to wp-config.php |
| Database Connection | None | “Error establishing database connection” | Incorrect credentials in wp-config.php | Check DB_NAME, DB_USER, DB_PASSWORD, DB_HOST |
| Upload File Size | None | File exceeds maximum upload size | Upload limit too low | Edit php.ini or compress files |
| Execution Time Exceeded | None | “Maximum execution time exceeded” | Task takes too long | Add max_execution_time = 60 to php.ini |
| Failed Auto-Upgrade | None | Update fails and breaks site | Failed automatic update | Disable plugins, manual update, backup first |
| Write to Disk Failed | None | “Failed to write file to disk” | Incorrect file permissions, server issues | Check folder permissions (755/777), verify server |
| Connection Timed Out | None | “Connection timed out” | Server limitations on shared hosting | Deactivate plugins, use default theme, increase memory |
| Secure Connection Error | None | Can’t connect to WordPress.org | Settings not configured correctly | Wait, contact hosting provider |
| Maintenance Mode Stuck | None | “Briefly unavailable for scheduled maintenance” | .maintenance file not removed | Delete .maintenance file via FTP |
| Cloudflare Error 521 | 521 | “521 Web Server Down” | Connection trouble to server | Check server status, verify firewall settings |
| Images Not Working | None | Broken images, media library mess | Plugin conflicts, file permissions | Disable recent plugins, set permissions to 755 |
| File Type Not Permitted | None | Upload restricted | WordPress security restrictions | Use “File Upload Types” plugin |
| Syntax Errors | None | Error message with file/line | Code mistakes, typos in custom code | Find file/line, undo changes, enable debug mode |
| SSL Errors | None | SSL setup issues | Certificate not configured correctly | Use host SSL installer, ensure HTTPS, renew certificate |
| Corrupted Database | None | “Error Establishing Database Connection” | Corrupted database file | Restore backup or add WP_ALLOW_REPAIR to wp-config.php |
| Destination Folder Exists | None | “Destination folder already exists” | Plugin/theme previously installed | Delete folder via FTP, reinstall |
| Admin Lockout | None | Can’t access admin page | Password typo, .htaccess issues | Reset password, check .htaccess, create new user via phpMyAdmin |
| PHP Errors | None | Warning/message at dashboard top | PHP issues in code | Messages for PHP experts, site still runs for visitors |
| Chrome “Not Secure” | None | “Not Secure” next to address | No SSL certificate | Add SSL certificate to website |
| Import Problems | None | Import fails, takes too long | File too large, not enough space | Use faster connection, try WP-CLI, increase timeout |
How to use this guide:
- Find your error message or status code in the table
- Check the “Main Cause” column to understand what’s happening
- Apply the “Quick Fix” solution
- Scroll down to the matching section below for step-by-step instructions.
Common WordPress Errors and How to Fix Them
Absolutely, let’s simplify and make these common WordPress errors easy to understand.
1. The White Screen of Death
Your website displays an entirely blank screen – no content, no navigation, nothing. Sometimes you’ll see a brief error message. This happens when plugins conflict, themes break, or PHP memory is exhausted. It’s fixable in 5-10 minutes once you identify the cause.”
2. 400 Errors
400-series errors indicate client-side problems – issues with how your browser communicates with the server. Each specific code reveals a different issue: 400 indicates malformed requests, 401 requires authentication, 403 blocks access due to insufficient permissions, 404 indicates a page doesn’t exist, and 429 blocks too many requests from a single source.
A. 400 Bad Request
- Your server encounters a problem but cannot identify the cause.
- Mistyped website address, browser cache issues, or server configuration errors.
- Clear browser cache/cookies, check URL accuracy, flush DNS cache, disable extensions, and try incognito mode.
B. 403 Forbidden

- Security features block access to your site or specific resources.
- Incorrect file permissions (755/644), .htaccess rules, security plugins, CDN blocks, or hotlink protection.
- Set directories to 755, files to 644, regenerate .htaccess, disable security plugins temporarily, and check CDN settings.
C. 404 Not Found
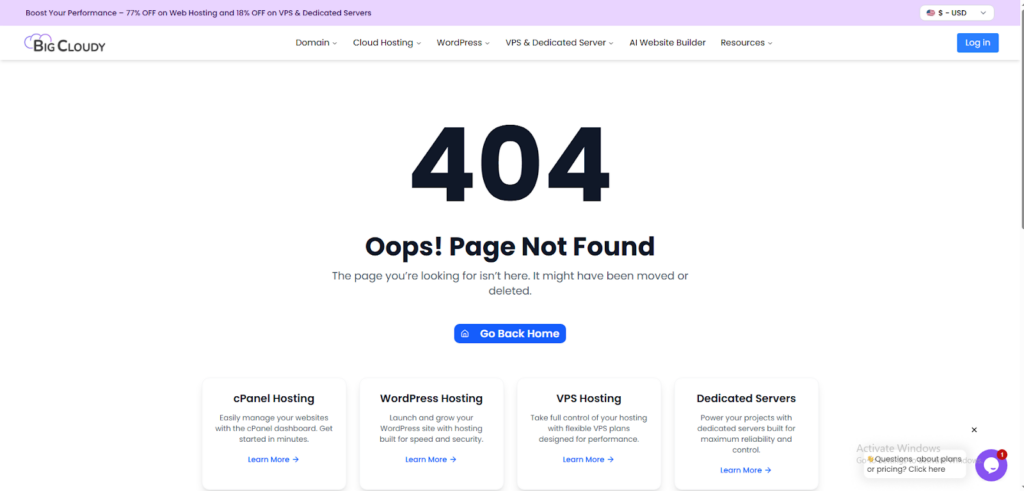
- The requested web page doesn’t exist at the specified location.
- Regularly fix broken links and use redirects when you change or delete pages.
D. 405 Method Not Allowed
- Your server rejects the browser’s request method.
- Check recent theme and plugin updates, server settings, and application code for issues.
E. 413 Request Entity Too Large
- The server cannot process requests exceeding size limitations.
- Attempting to upload files beyond the maximum allowed size.
- Increase the maximum request size through server configuration.
F. 429 Too Many Requests
- Server blocks multiple access attempts within short timeframes.
- Protection mechanism against suspicious or automated activity.
- Change the login page URL and test for theme and plugin conflicts.
3. Internal Server Error

Errors numbered between 500 and 599 indicate your website’s server is experiencing difficulties fulfilling requests. These represent various server-side issues requiring different troubleshooting approaches.
A. WordPress 500 Internal Server Error
- This error blocks site access and harms search engine rankings.
- Multiple potential causes make diagnosis challenging. Start by clearing the browser cache and reloading the page. If unsuccessful, pursue more technical troubleshooting steps.
B. 501 Not Implemented
- Your server doesn’t support the functionality required by the browser’s request.
- Similar to 500 errors, it negatively impacts search engine rankings. Try reloading the page, clearing browser cache, and disabling browser extensions. Contact the hosting provider if issues persist.
C. 502 Bad Gateway
- This error can occur when one server is assisting another, and something goes wrong.
- It’s bad for SEO, so you should fix it quickly. Try reloading the page, clearing your browser history, and turning off any special settings. If that doesn’t work, check your DNS settings or ask your hosting company for help, especially.
- When you see this, your server is up, but it can’t be reached.
- It won’t affect your search engine ranking, but it’s frustrating for visitors. You can turn off your website’s plugins, switch to a basic design, or check whether your server needs more resources. If none of these work, talk to your hosting company.
E. 504 Gateway Timeout
- This error is similar to the 502 error and occurs when servers have trouble communicating with each other.
- It can hurt your SEO, so try reloading the page, turning off special browser settings, and checking your DNS settings. You can also temporarily disable your content delivery network (CDN). If none of these steps resolves the issue, contact your hosting company.
4. Memory Limit Error
WordPress requires server memory (RAM) to process requests. Your hosting plan allocates a specific PHP memory limit (often 128MB or 256MB by default). When plugins, themes, or processes exceed this limit, you’ll see: ‘Fatal error: Allowed memory size exhausted.
Fix this by increasing the PHP memory limit in wp-config.php:
php
define(‘WP_MEMORY_LIMIT’, ‘256M’);
For the admin area specifically:
php
define(‘WP_MAX_MEMORY_LIMIT’, ‘512M’);
Contact hosting support if file edits don’t work – they may enforce server-level restrictions.
5. Error Establishing Database Connection
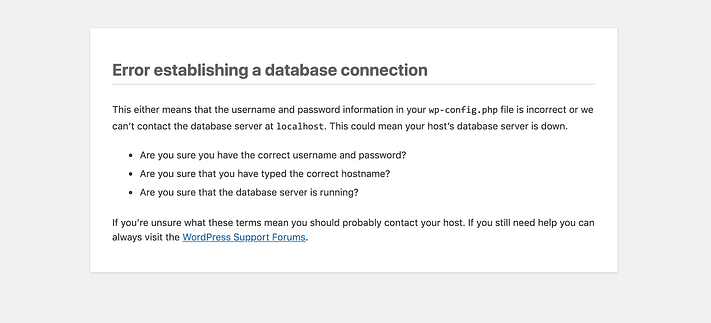
When WordPress cannot connect to your MySQL/MariaDB database, you’ll see: ‘Error establishing a database connection.’ This blocks all site access and admin dashboard functionality.
Common causes:
- Incorrect database credentials in wp-config.php
- Database server down/overloaded
- Corrupted database tables
- Exceeded hosting database connection limits
First check wp-config.php for correct DB_NAME, DB_USER, DB_PASSWORD, and DB_HOST values matching your hosting control panel database settings
6. Exceeded Maximum Upload File Size
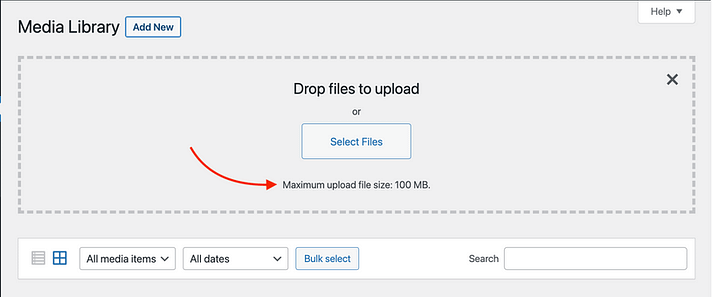
Your WordPress site has a limit on how big the files you can upload can be. If you try to upload a file that’s too large, you’ll get an error message. To check your limit, follow these steps:
- Firstly, go to your WordPress dashboard.
- Then navigate to the Media section and click “Add New.”
- Look for the maximum file size limit displayed. This is the largest file you can upload.
- If you need to upload larger files, consider these options:
- Adjusting php.ini: You can increase your upload size limit by editing the php.ini file on your server. However, please note that this method may not work for all wordpress hosting plans, so consult your hosting provider.
- File Compression: If increasing the limit isn’t possible, consider compressing your files before uploading them to reduce their size.
7. Maximum Execution Time Exceeded
When your website performs tasks, it has a time limit to complete them. If it takes too long, it stops, and the task fails. To resolve this issue, you can make changes to a file called php.ini:
- Open your php.ini file.
- Add the line:
max_execution_time = 60
(This sets the maximum execution time to 60 seconds).
- Then save the file.
However, please be aware that this solution may not work in all cases, so it’s advisable to consult your hosting provider for assistance.
8. Failed Auto-Upgrade
Automatic updates sometimes fail and damage your WordPress website. Perform manual updates with proper precautions for safe upgrades:
- Disable all plugins before updating
- Switch to the default WordPress theme, like Twenty Twenty-Four
- Follow WordPress’s manual update instructions carefully
- Create a website backup before updating to safeguard data
9. Failed to Write File to Disk
If you encounter the “Upload: Failed to write file to disk” error when uploading media files, it’s usually due to incorrect file permissions or server issues. Here’s how to address it:
- Check File Permissions: Ensure that the folder where you’re uploading files has the correct permissions (usually 755 or 777 for directories and 644 for files).
- Verify Server Status: If the issue persists, it may be due to server issues. Contact your hosting provider to investigate and resolve any server-related problems.
10. Connection Timed Out
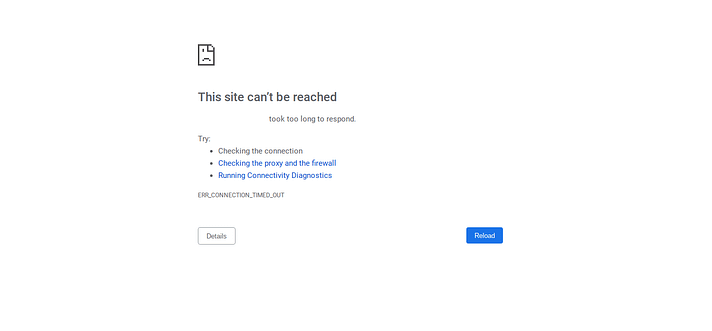
Server limitations can result in a “connection timed out” error, especially on shared hosting plans. Here are the steps to troubleshoot and resolve this issue:
- Deactivate Plugins: Start by deactivating all your WordPress plugins, then reactivating them one by one to determine whether a particular plugin is causing the issue.
- Use Default Theme: While testing, switch to a default WordPress theme, such as Twenty Twenty-One, to rule out theme-related issues.
- Increase Memory Limit: Increase your PHP memory limit, as insufficient memory can cause timeouts. Consult your hosting provider or edit your php.ini file to adjust the memory limit.
11. Secure Connection Error
A secure connection error occurs when your website’s settings aren’t configured correctly, preventing your site from connecting to WordPress.org. This can stop you from updating your core files. Unfortunately, there’s no quick fix for these WordPress errors. Sometimes, you have to wait for a little while, and the problem might go away on its own. If it doesn’t, you can contact your web hosting provider for assistance.
12. Stuck in Maintenance Mode
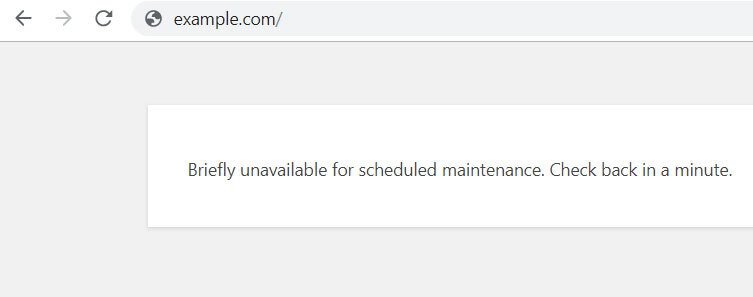
Updating your website’s core software is crucial for security. WordPress uses a special file called “.maintenance” during updates, but it sometimes isn’t properly removed, leaving your site stuck in maintenance mode. Fortunately, fixing this is straightforward:
- Firstly, use an FTP client to connect to your website’s server.
- Find the “.maintenance” file in your main folder and delete it.
- Your site should go back to normal once you’ve deleted the file.
13. Cloudflare Error 521
Cloudflare is a helpful security and speed service, but it can sometimes have trouble connecting to your server, resulting in a 521 error. To solve this:
- Make sure your server is up and running.
- Check if your server’s firewall is blocking Cloudflare’s IP addresses.
- If needed, contact your web hosting provider for assistance.
14. Images Aren’t Working

Occasionally, WordPress images may not display correctly. If your media library looks like a mess, you might be dealing with broken media files. Various factors, such as plugins or file permission issues, can cause this:
- If you recently added or updated a plugin, try disabling it to see if it’s causing the problem.
- Ensure that your file permissions for uploads are set to 755.
- If these steps don’t work, consider checking for security issues and reaching out to your hosting provider for help.
15. File Type or Page Access Not Permitted
Overall, WordPress restricts some file types to protect your site from security threats. However, this can sometimes prevent users from uploading harmless files. Therefore, to allow more file types, you can use a free plugin like “File Upload Types”.
16. WordPress Syntax Errors
Syntax errors happen when there are problems with the code structure on your site. This usually occurs when you:
- Recently added custom code with mistakes (like typos).
- Installed a new plugin or theme with coding errors.
To troubleshoot, look for the file and line causing the issue. If you can’t find it, try undoing recent code changes or disabling new plugins/themes. You can also enable WordPress debug mode to help identify the problem.
17. SSL Errors
SSL certificates indeed enhance website security. However, setting them up can lead to various WordPress errors. To prevent these issues, configure your certificate correctly from the start. Use your hosting provider’s SSL certificate installer tool, ensure your site uses HTTPS, and renew your SSL certificate when necessary.
18. Corrupted Database
A corrupted file can especially disrupt your WordPress site, resulting in WordPress errors like “Error Establishing Database Connection.” To fix this, restore a backup of your site or add this code to your “wp-config.php” file:
‘WP_ALLOW_REPAIR’, true
Afterwards, your site should return to normal.
19. The Destination Folder Already Exists
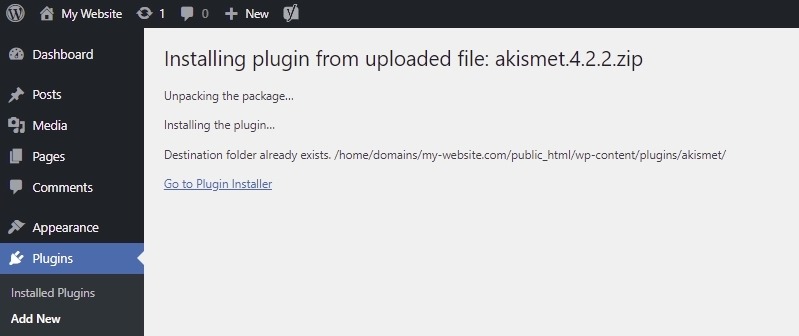
When installing a plugin or theme, you might encounter a “Destination folder already exists” error. This typically means the program was previously installed. To resolve it:
- Use your FTP client to access the ”wp-content” folder.
- Find the folder with the program’s name, delete it, and try the installation again.
- Note: Recent WordPress versions allow you to reinstall themes or plugins, even if they are already installed, making this error less common.
20. Locked Out of Your Admin Page
Being locked out of your admin page can be frustrating. Various factors can cause this, from a password typo to issues with your “.htaccess” file. To regain access:
- Refer to a troubleshooting guide.
- Manually change your admin password.
- Create a new admin user using phpMyAdmin.
In other words, these steps can help you regain control of your WordPress website.
21. PHP Errors on WordPress
If something goes wrong with the PHP on your WordPress site, you’ll notice a message or a warning at the top of your WordPress dashboard. This message tells you by all means what the problem is and which files it’s affecting.
These messages are mainly for people who know how to work with PHP and can fix the issue in the website’s code. If you’re not familiar with PHP, trying to fix these errors on your own might make things worse for your site.
But here’s the good news: PHP errors won’t make your site stop working or keep people from using it. So, you can relax knowing that your site is still up and running for your visitors.
22. Chrome’s “Not Secure” Warning
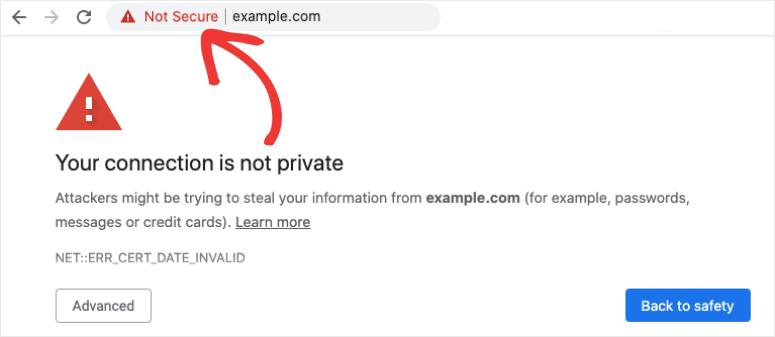
When you use Google Chrome to surf the web, you might have seen a message saying ‘Not Secure’ next to some website addresses:
This message pops up because the website doesn’t have something called an SSL certificate. If your website triggers these messages in visitors’ browsers, it can undermine your site’s trustworthiness, reduce visitor numbers, affect your search engine rankings, and make it harder to convert visitors into customers. To avoid this, you can add an SSL certificate to your website.
Recently, Chrome also started showing a warning called ERR_SSL_OBSOLETE_VERSION for websites that don
23. WordPress Import Problems
Sometimes, you need to bring content into your WordPress site, and that’s normal. Many developers explicitly use plugins to do this. But there can be problems, such as your computer taking too long to load or running out of space.
Here’s how to make it work better:
- Use a faster internet connection if you can.
- Try a tool called WP-CLI to import your stuff.
- If your computer stops too soon, you can make it wait longer by increasing the PHP timeout limit.
Conclusion
In conclusion, troubleshooting WordPress errors is a crucial skill for website owners and developers. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can efficiently diagnose and resolve common WordPress errors, ensuring your site remains reliable, secure, and user-friendly.
Remember that WordPress errors are a regular part of website maintenance, but with the proper knowledge and tools, you can tackle them like a pro and keep your website running smoothly.
FAQs
The most frequent cause is a Plugin or Theme Conflict. This occurs after updating an old item or installing a new one, leading to significant issues such as the White Screen of Death (WSOD). Always test new installations on a staging site first to avoid breaking your live website.
Don’t panic; immediately follow these steps:
1. Clear all server and plugin caching.
2. Verify your database credentials in the
wp-config.php file.
3. Temporarily disable all
plugins
by renaming the plugins folder via FTP to check for a conflict.
Server errors are typically identified by 503 Service Unavailable or 504 Gateway Timeout responses, indicating an overload or a firewall issue. Errors such as WSOD or “Error Establishing Database Connection” usually indicate issues with WordPress files, themes, or database credentials. If it’s a 500-level error not resolved by disabling plugins, contact your host.
This is a widespread issue caused when the server loses the correct instructions for handling custom links (permalinks). The fix is simple: Log into your WordPress Dashboard, go to Settings → Permalinks, and click “Save Changes”. This forces WordPress to rebuild the necessary .htaccess file. If you prefer, our team can handle this for you as part of our free website migration service.
The safest method is to use a Staging Environment – an exact, private copy of your live website. Perform the update on the staging site first to catch any errors. If successful, use your hosting panel to push the changes safely to your live site with zero risk.